IAV’s Multi-Purpose 3D Coupling Solution for Electro-Physicochemical Battery Models via COMSOL API
The development of batteries for automotive application is progressing rapidly. It goes hand in hand with a rising demand for scarce raw materials. Diversification of cell chemistries is a promising approach to respond to market fluctuations and at the same time minimize system costs. A highly integrated model-based development process can be used to investigate the potential of different cell-chemistries, designs, and cooling concepts. It reduces the need for physical prototypes and allows for performance optimization towards typical requirements of automotive applications.
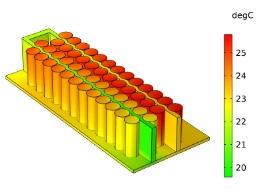
The focus of this presentation is placed on thermal management of the battery and cooling system design. The temperature of a cell does impact its electrochemical behavior (e.g., performance, aging) which in turn influences its heat losses and the coolant temperature. It is necessary to couple the simulation domains of the cell, the cooling system, and the 3D battery thermal boundary conditions to optimize its operation.
In this study two pseudo-two-dimensional (P2D) battery cell models roughly based on the COMSOL Application Galleries model “1D Lithium-Ion Battery Model for the Capacity Fade Tutorial”, (Battery Design Module) are developed. They are used to analyze the electrochemical behavior and optimize the design of two substantially different chemistries at cell level: A sodium-ion and a solid-state lithium-ion cell. In a next step the electrochemical performance of these cells is investigated at vehicle level to account for system interactions over varying boundaries (e.g., temperature).
To achieve this, the cell-models were integrated into simplified 3D partial battery pack thermal models including cooling circuits. These are packaged into Apps using the Application Builder along with interfacing Java® code using the COMSOL API and optimally compiled with COMSOL Compiler™. These Apps are then coupled to vehicle simulation environments in 3rd party software (e.g., GT-SUITE) for Co-simulation.
Vehicle simulation environments define model inlets and boundary conditions (e.g., inlet current, coolant inlet temperature and mass flow, heat rates at boundary surfaces and initial conditions). The COMSOL® app returns voltage, SOC, temperatures, and power dissipation and makes all internal cell states available for interpretation as needed.
This multi-purpose 3D coupling approach greatly extends the possibilities in using COMSOL® battery models for automotive system development as the use of the Application Builder in conjunction with COMSOL Compiler™ makes this approach readily available for model-based development within many existing Toolchains.
This presentation is based on published work presented at the International Vienna Motor Symposium in April 2023 [1].
Download
- Hilgert_4791_presentation.pdf - 1.87MB
